McKinsey Plots Thousands of Job Cuts in Slowdown for Consulting Industry
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.

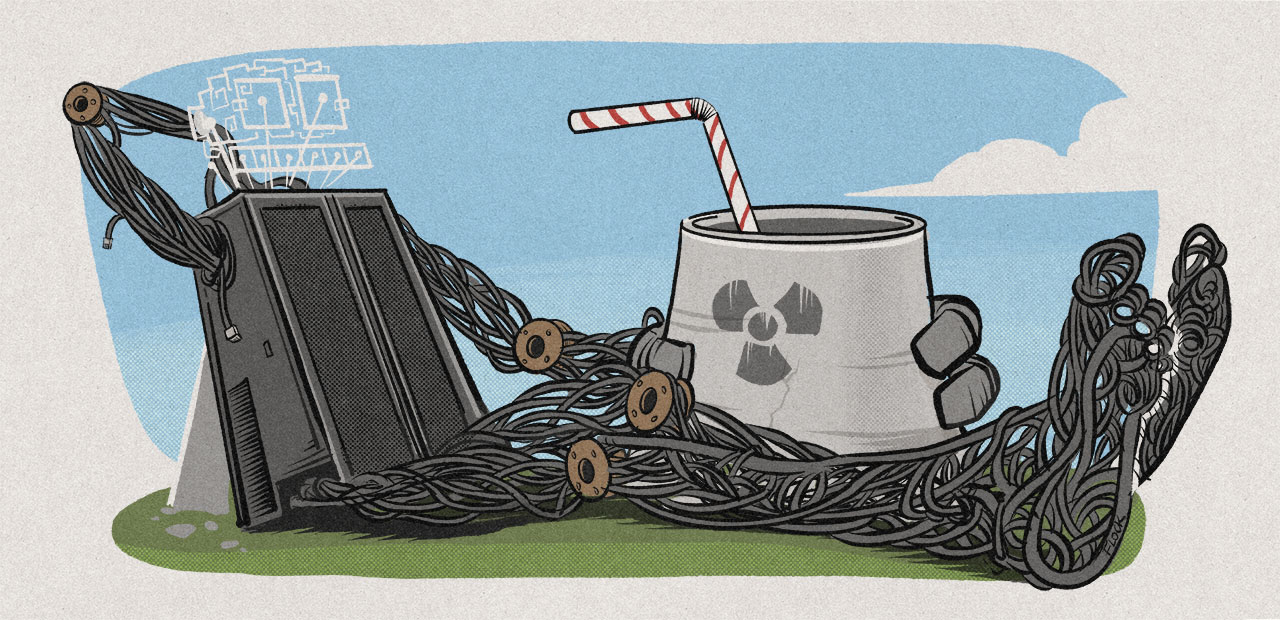
En diffusant des publicités à destination des pays extérieurs à la Chine, les entreprises chinoises forment l’une des principales sources de revenus publicitaires pour Meta. Alors qu’elles produisent un taux de publicités frauduleuses inégalé, la société de Mark Zuckerberg semble minimiser ses efforts de modération.
La Chine n’est pas un marché simple, pour Meta. La société de Mark Zuckerberg a beau s’être plié en quatre pour plaire aux autorités locales – y compris, accuse son ex-directrice des politiques publiques Sarah Wynn-Williams, en créant tout un système de censure –, Facebook, Instagram et consorts n’en sont pas moins interdits à la population locale depuis 2009.
Ce qui n’est pas interdit, en revanche, c’est de faire de la publicité sur ces plateformes, à destination d’un public étranger. Ce système publicitaire permet à des entreprises chinoises de toucher des millions de consommateurs à travers le globe, mais aussi de représenter 11 % du chiffre d’affaires global de Meta. Selon des documents internes obtenus par Reuters, Shein et Temu étaient les deux plus gros clients publicitaires de Meta dans le monde en 2024, devant Amazon.
Problème : près d’une publicité sur cinq promues sur Facebook, Instagram et consorts depuis la Chine constituent des violations flagrantes de ses conditions d’utilisation. 19 % de ces publicités consistent en des contenus de promotions d’arnaques, de jeux illégaux, ou encore de produits interdits.
Début novembre, une précédente enquête démontrait qu’à travers la planète, Meta réalisait près de 10 % de son chiffre d’affaires annuel, soit environ 16 milliards de dollars l’an dernier, à partir de publicités enfreignant ses propres politiques. En Europe, en revanche, l’entreprise a pris le parti d’adopter une lecture étendue du récent règlement sur la transparence et le ciblage de la publicité à caractère politique, pour y empêcher la publicité « politique, électorale et sur les sujets sociaux », privant des acteurs a priori légitimes d’un outil qu’ils utilisaient jusqu’ici régulièrement.
Rien qu’entre 2022 et 2024, les revenus publicitaires chinois ont fait plus que doubler, passant de 7,5 milliards de dollars à 18,4 milliards de dollars, pour atteindre près de 10 % du chiffre d’affaires global de Meta. En parallèle, il devenait de plus en plus évident qu’une large part de ces activités constituaient des pratiques frauduleuses.
En interne, Meta calcule que l’équivalent du quart de toutes les publicités frauduleuses diffusées dans ses systèmes viennent de Chine, selon les documents obtenus par Reuters. Un tel taux de fraude se traduit aussi en montant de revenus : au total, Meta aurait gagné près de 3 milliards de dollars en diffusant via ses systèmes publicitaires des contenus promouvant des arnaques, de la pornographie ou d’autres contenus illégaux.
Pendant la « Golden Week », des congés dont des millions de citoyens chinois profitent au mois d’octobre, le taux d’arnaques sur les plateformes de Meta décline à l’échelle mondiale.
Les victimes, elles, se situent partout sur le globe, d’acheteurs taïwanais qui se retrouvent avec des compléments alimentaires inadaptés aux investisseurs d’Amérique du Nord allégés de leurs économies à la suite d’une arnaque quelconque. L’ampleur du problème est telle qu’en 2024, des équipes de la société de Mark Zuckerberg ont déclaré qu’il était nécessaire de réaliser « des investissements significatifs pour réduire ces dommages grandissants ». Pendant la seconde moitié de l’année 2024, une nouvelle équipe anti-fraude affectée spécifiquement à ce défi a réussi à réduire le total des publicités frauduleuses de 19 % à 9 % du chiffre d’affaires publicitaire total issu de Chine.
Et puis, à la fin de l’année passée, un nouveau document indiquait qu’à la suite d’un « revirement de la stratégie d’intégrité et du suivi de Zuck » (sic), l’équipe en question était « invitée à suspendre » ses activités. Auprès de Reuters, un porte-parole indique que Mark Zuckerberg n’a pas demandé la dissolution de l’équipe, mais de redoubler des efforts pour lutter contre les escroqueries « partout dans le monde ».
Dans un document de février 2025, des dirigeants de Meta écrivaient quoi qu’il en soit renoncer à chercher la « parité » entre la lutte contre la fraude publicitaire en Chine et ailleurs dans le monde. Alors que sa précédente tentative avait été proche de ramener le taux de fraude venu de Chine à une proportion similaire à celle constatée ailleurs, les efforts ont été abandonnés, au motif que le marché chinois serait spécifiquement « antagoniste ».
À la mi-2025, le phénomène avait repris une nouvelle ampleur, les publicités contrevenant aux politiques de Meta formant à nouveau 16 % des revenus de l’entreprise en Chine, pays qualifié sur certaines présentations de principal « pays exportateur d’escroqueries ».
Pour faire vivre son activité publicitaire malgré les restrictions, Meta passe par un système spécifique à la Chine. Sur place, l’entreprise vend l’essentiel de ses publicités via 11 agences principales, qu’il qualifie dans des documents de « plus gros revendeurs » (top tier resellers).
Ces partenaires s’occupent ensuite d’animer un réseau de plus petites agences chinoises ou extérieures au pays, ou de vendre elles-mêmes des publicités. Les agences de deuxième niveau, elles, interagissent à leur tour avec une myriade de petites sociétés qui n’ont pas de lien direct avec Meta ou ses 11 plus grands partenaires. D’après ses documents internes, ce réseau complexe et opaque favorise la prolifération de publicités problématiques, promouvant des arnaques, des jeux illégaux ou des produits interdits.
Un audit de la société Propellerfish constate notamment la facilité avec laquelle un publicitaire peut se créer un compte utilisateur sur Facebook ou Instagram (un nom et une date de naissance suffisent), ou encore la multiplication de faux comptes. Le rapport souligne aussi l’éclosion d’une industrie complète de « spécialistes de l’optimisation publicitaire », dont le fonctionnement complet repose sur l’exploitation de failles dans les systèmes de vérification de Meta et sur la création et la diffusion de publicités pour des arnaques et des biens illégaux. Dans la mesure où ces contenus ne visent pas le public chinois, les autorités locales tendent à laisser faire, constate encore Propellerfish.
La modération des publicités est, elle aussi, sous-traitée aux partenaires de Meta. Dans la mesure où les entreprises ne peuvent pas atteindre normalement Facebook ou Instagram, Meta paie une commission de près de 10 % à ses 11 partenaires principaux pour que ces derniers permettent à leurs partenaires d’acheter des publicités et de les placer sur les plateformes dirigées par Mark Zuckerberg. Les publicités acquises par ces canaux profitent par ailleurs de protections spécifiques. Sur le terrain, relève Reuters, certains des grands partenaires de Meta en viennent à promouvoir explicitement leur capacité à outrepasser les contrôles de l’entreprise états-unienne.
Auprès de Reuters, un porte-parole de Meta indique que les systèmes de l’entreprise ont bloqué 46 millions de publicités soumises par ses partenaires chinois dans les 18 derniers mois, généralement avant que le public n’y soit exposé, et que cela faisait partie intégrante de ses processus habituels de modération.

L’EPR de Flamanville est monté à 100 % de sa capacité ce week-end. Les tests vont continuer, mais une lourde opération de maintenance est déjà programmée pour septembre 2026 : 350 jours d’arrêt pour notamment remplacer le couvercle de la cuve, une petite pièce de… 100 tonnes. Le réacteur a déjà vu les délais et son coût exploser dans les grandes largeurs.
Vendredi, l‘ASNR (Autorité de sûreté nucléaire et de radioprotection) donnait son accord « pour le passage du réacteur EPR de Flamanville à un niveau de puissance supérieur à 80 % de sa puissance nominale ». En clair, le réacteur peut monter jusqu’à 100 % de sa puissance maximale de fonctionnement. On est encore loin d’une mise en production pérenne.
Au début de l’année, le réacteur avait eu le droit de dépasser les 25 % de puissance. L’ASNR avait ensuite procédé à des inspections, sans mettre « en évidence d’élément susceptible de remettre en cause la possibilité de poursuivre la montée en puissance du réacteur ». Le réacteur avait pour rappel produit ses premiers électrons en décembre 2024, après avoir obtenu l’autorisation de mise en service quelques mois auparavant. Le réacteur avait alors produit 100 MW de puissance électrique, loin des plus de 1 600 MW prévus.
Dans la foulée de l’autorisation, EDF a poussé les curseurs. Dimanche 14 décembre 2025, la pleine puissance a été atteinte à 11h37 se félicite l’entreprise : « le réacteur de Flamanville 3 […] a produit 1 669 MW de puissance électrique brute ».
On parle de puissance brute, en opposition à la puissance nette qui est celle injectée dans le réseau. EDF rappelle que la puissance nucléaire d’un réacteur correspond à la quantité totale de chaleur produite dans le cœur du réacteur par la fission nucléaire ; à ne pas confondre avec la fusion, qui est en cours de développement. La « chaleur sert à produire de la vapeur qui fera tourner la turbine. Elle est exprimée en MW thermiques (MWth) ».
Quand on parle de puissance électrique brute, c’est la puissance maximale en sortie de turbine, qui « entraîne un alternateur chargé de convertir l’énergie mécanique en électricité ». Dans la pratique, un « réacteur nucléaire consomme une partie de l’électricité qu’il produit pour ses propres besoins de fonctionnement (pompes, systèmes de ventilation, circuits de sûreté…) ».
Cette montée en puissance devait avoir lieu plus tôt dans l’année, mais un problème détecté en juin a repoussé l’échéance de plusieurs mois : « l’unité de production n°3 de Flamanville a été mise à l’arrêt dans le cadre des essais de mise en service du réacteur. Suite à des analyses, le réacteur de Flamanville est maintenu à l’arrêt pour intervenir sur des soupapes de protection du circuit primaire principal ». Tout est rentré dans l’ordre fin octobre.
Attention, le réacteur est en phase de test, la production de masse de manière pérenne n’est pas encore là. Il est question de « tester les matériels à pleine puissance, réaliser des relevés et vérifier leur bon fonctionnement ». Sur les réacteurs nucléaires, le rodage est long. Au cours des prochaines semaines, « la puissance du réacteur sera amenée à varier pour poursuivre les essais à différents paliers de puissance et une intervention sera réalisée sur un poste électrique interne ».
L’EPR va aussi avoir droit à des travaux de plus grande envergure avec le remplacement du couvercle de la cuve, une pièce de 100 tonnes et 6 mètres de diamètre. Cette opération se fera lors du premier arrêt pour rechargement du réacteur, prévu pour septembre 2026. Elle doit durer la bagatelle de 350 jours, quasiment une année complète. Le démarrage ne devrait donc pas avoir lieu avant fin 2027.
En 2017, l’ASNR avait expliqué que cette « anomalie concerne le fond et le couvercle de la cuve. L’acier de ces composants n’a pas la composition chimique attendue. Au cours de leur fabrication par forgeage, l’usine Creusot Forge d’Areva NP n’a pas suffisamment éliminé une zone qui contient naturellement un excès de carbone […]. Cette zone se retrouve donc au centre des pièces finales ».
Comme nous l’avons déjà expliqué, l’Autorité considère que, sur la base de ces analyses techniques, « les caractéristiques mécaniques du fond et du couvercle de la cuve sont suffisantes au regard des sollicitations auxquelles ces pièces sont soumises, y compris en cas d’accident ». Il fallait compter environ 7 ans pour construire un nouveau couvercle, l’ASNR avait donc donné son feu vert jusqu’à fin 2024 en attendant que la pièce soit disponible. La date limite a ensuite été repoussée.
Pour la cuve, la revue technique était arrivée à la conclusion que « l’anomalie ne remet pas en cause l’aptitude au service ». Pierre-Franck Chevet, président de l’ASNR en 2017, affirmait qu’« on peut se prononcer favorablement sur l’utilisation pérenne du fond de cuve ». Si la cuve était à changer, les coûts et les délais auraient explosé… enfin davantage de ce qu’ils sont déjà.
Le réacteur a pour rappel été mis en marche après pas moins de 17 ans de travaux (12 ans de retard sur le calendrier initial) et une explosion des coûts… c’est peu de le dire. De 3 milliards d’euros, l’addition est passée à… plus de 20 milliards d’euros.
Dans un nouveau rapport publié au début de l’année, la Cour des comptes affirmait que « les calculs effectués par la Cour aboutissent à une rentabilité médiocre pour Flamanville 3, inférieure au coût moyen pondéré du capital de l’entreprise, sur la base d’un coût total de construction estimé à environ 23,7 milliards d’euros (intérêts intercalaires compris) ». En 2020 déjà, la Cour tirait à boulet rouge sur le nucléaire français.
Récemment, RTE appelait à accélérer les usages électriques (voitures, datacenters, hydrogène) afin d’assurer un meilleur équilibre entre consommation et production d’électricité. La raison, selon RTE : une consommation « atone » depuis la pandémie de Covid-19 alors que la production d’énergies renouvelables (hydraulique comprise) et nucléaire ont progressé. La mise en marche de l’EPR de Flamanville va encore augmenter la capacité de production de la France.
Les chercheurs et chercheuses qui travaillent sur des images peuvent dès à présent les inclure dans les articles en open access en se posant moins de questions.
Le ministère de la Recherche a mis en place une « licence collective étendue » qui facilite l’utilisation d’images dans les publications en accès ouvert, explique-t-il.
Cette licence est issue d’une convention passée avec les organismes de gestion collective des droits d’auteur : ADAGP (Société des auteurs dans les arts graphiques et plastiques), SAIF (Société des Auteurs des arts visuels et de l’Image Fixe), Scam (Société civile des auteurs multimédia).
« Cette mesure bénéficie particulièrement aux disciplines où l’image est un objet d’étude essentiel, comme l’Archéologie, la Géographie, l’Histoire, l’Histoire de l’Art ou encore la Sociologie. Elle s’applique également aux Sciences, Technologies et en Médecine, lorsque les images utilisées ne sont pas produites en laboratoire », explique le ministère.

Jusqu’à récemment une telle chose n’était pas possible, mais l’article 28 de la loi de programmation de la recherche de 2020 prévoit que le gouvernement puisse prendre des ordonnances pour modifier le Code de la propriété intellectuelle « aux fins de permettre l’octroi de licences collectives ayant un effet étendu ». Une ordonnance a ensuite été prise en 2021.
Les chercheurs, notamment ceux en sciences humaines et sociales qui travaillent sur des images, devaient effectuer des « démarches complexes image par image : identification des ayants droit, demandes d’autorisation, contractualisation et paiement », explique le ministère. Désormais, ils devront seulement signaler l’image utilisée à l’aide d’un formulaire.
Pour cette licence, le ministère explique assurer « un paiement forfaitaire aux ayants droit » sans donner d’information sur le montant et les diverses conditions de la convention.

En diffusant des publicités à destination des pays extérieurs à la Chine, les entreprises chinoises forment l’une des principales sources de revenus publicitaires pour Meta. Alors qu’elles produisent un taux de publicités frauduleuses inégalé, la société de Mark Zuckerberg semble minimiser ses efforts de modération.
La Chine n’est pas un marché simple, pour Meta. La société de Mark Zuckerberg a beau s’être plié en quatre pour plaire aux autorités locales – y compris, accuse son ex-directrice des politiques publiques Sarah Wynn-Williams, en créant tout un système de censure –, Facebook, Instagram et consorts n’en sont pas moins interdits à la population locale depuis 2009.
Ce qui n’est pas interdit, en revanche, c’est de faire de la publicité sur ces plateformes, à destination d’un public étranger. Ce système publicitaire permet à des entreprises chinoises de toucher des millions de consommateurs à travers le globe, mais aussi de représenter 11 % du chiffre d’affaires global de Meta. Selon des documents internes obtenus par Reuters, Shein et Temu étaient les deux plus gros clients publicitaires de Meta dans le monde en 2024, devant Amazon.
Problème : près d’une publicité sur cinq promues sur Facebook, Instagram et consorts depuis la Chine constituent des violations flagrantes de ses conditions d’utilisation. 19 % de ces publicités consistent en des contenus de promotions d’arnaques, de jeux illégaux, ou encore de produits interdits.
Début novembre, une précédente enquête démontrait qu’à travers la planète, Meta réalisait près de 10 % de son chiffre d’affaires annuel, soit environ 16 milliards de dollars l’an dernier, à partir de publicités enfreignant ses propres politiques. En Europe, en revanche, l’entreprise a pris le parti d’adopter une lecture étendue du récent règlement sur la transparence et le ciblage de la publicité à caractère politique, pour y empêcher la publicité « politique, électorale et sur les sujets sociaux », privant des acteurs a priori légitimes d’un outil qu’ils utilisaient jusqu’ici régulièrement.
Rien qu’entre 2022 et 2024, les revenus publicitaires chinois ont fait plus que doubler, passant de 7,5 milliards de dollars à 18,4 milliards de dollars, pour atteindre près de 10 % du chiffre d’affaires global de Meta. En parallèle, il devenait de plus en plus évident qu’une large part de ces activités constituaient des pratiques frauduleuses.
En interne, Meta calcule que l’équivalent du quart de toutes les publicités frauduleuses diffusées dans ses systèmes viennent de Chine, selon les documents obtenus par Reuters. Un tel taux de fraude se traduit aussi en montant de revenus : au total, Meta aurait gagné près de 3 milliards de dollars en diffusant via ses systèmes publicitaires des contenus promouvant des arnaques, de la pornographie ou d’autres contenus illégaux.
Pendant la « Golden Week », des congés dont des millions de citoyens chinois profitent au mois d’octobre, le taux d’arnaques sur les plateformes de Meta décline à l’échelle mondiale.
Les victimes, elles, se situent partout sur le globe, d’acheteurs taïwanais qui se retrouvent avec des compléments alimentaires inadaptés aux investisseurs d’Amérique du Nord allégés de leurs économies à la suite d’une arnaque quelconque. L’ampleur du problème est telle qu’en 2024, des équipes de la société de Mark Zuckerberg ont déclaré qu’il était nécessaire de réaliser « des investissements significatifs pour réduire ces dommages grandissants ». Pendant la seconde moitié de l’année 2024, une nouvelle équipe anti-fraude affectée spécifiquement à ce défi a réussi à réduire le total des publicités frauduleuses de 19 % à 9 % du chiffre d’affaires publicitaire total issu de Chine.
Et puis, à la fin de l’année passée, un nouveau document indiquait qu’à la suite d’un « revirement de la stratégie d’intégrité et du suivi de Zuck » (sic), l’équipe en question était « invitée à suspendre » ses activités. Auprès de Reuters, un porte-parole indique que Mark Zuckerberg n’a pas demandé la dissolution de l’équipe, mais de redoubler des efforts pour lutter contre les escroqueries « partout dans le monde ».
Dans un document de février 2025, des dirigeants de Meta écrivaient quoi qu’il en soit renoncer à chercher la « parité » entre la lutte contre la fraude publicitaire en Chine et ailleurs dans le monde. Alors que sa précédente tentative avait été proche de ramener le taux de fraude venu de Chine à une proportion similaire à celle constatée ailleurs, les efforts ont été abandonnés, au motif que le marché chinois serait spécifiquement « antagoniste ».
À la mi-2025, le phénomène avait repris une nouvelle ampleur, les publicités contrevenant aux politiques de Meta formant à nouveau 16 % des revenus de l’entreprise en Chine, pays qualifié sur certaines présentations de principal « pays exportateur d’escroqueries ».
Pour faire vivre son activité publicitaire malgré les restrictions, Meta passe par un système spécifique à la Chine. Sur place, l’entreprise vend l’essentiel de ses publicités via 11 agences principales, qu’il qualifie dans des documents de « plus gros revendeurs » (top tier resellers).
Ces partenaires s’occupent ensuite d’animer un réseau de plus petites agences chinoises ou extérieures au pays, ou de vendre elles-mêmes des publicités. Les agences de deuxième niveau, elles, interagissent à leur tour avec une myriade de petites sociétés qui n’ont pas de lien direct avec Meta ou ses 11 plus grands partenaires. D’après ses documents internes, ce réseau complexe et opaque favorise la prolifération de publicités problématiques, promouvant des arnaques, des jeux illégaux ou des produits interdits.
Un audit de la société Propellerfish constate notamment la facilité avec laquelle un publicitaire peut se créer un compte utilisateur sur Facebook ou Instagram (un nom et une date de naissance suffisent), ou encore la multiplication de faux comptes. Le rapport souligne aussi l’éclosion d’une industrie complète de « spécialistes de l’optimisation publicitaire », dont le fonctionnement complet repose sur l’exploitation de failles dans les systèmes de vérification de Meta et sur la création et la diffusion de publicités pour des arnaques et des biens illégaux. Dans la mesure où ces contenus ne visent pas le public chinois, les autorités locales tendent à laisser faire, constate encore Propellerfish.
La modération des publicités est, elle aussi, sous-traitée aux partenaires de Meta. Dans la mesure où les entreprises ne peuvent pas atteindre normalement Facebook ou Instagram, Meta paie une commission de près de 10 % à ses 11 partenaires principaux pour que ces derniers permettent à leurs partenaires d’acheter des publicités et de les placer sur les plateformes dirigées par Mark Zuckerberg. Les publicités acquises par ces canaux profitent par ailleurs de protections spécifiques. Sur le terrain, relève Reuters, certains des grands partenaires de Meta en viennent à promouvoir explicitement leur capacité à outrepasser les contrôles de l’entreprise états-unienne.
Auprès de Reuters, un porte-parole de Meta indique que les systèmes de l’entreprise ont bloqué 46 millions de publicités soumises par ses partenaires chinois dans les 18 derniers mois, généralement avant que le public n’y soit exposé, et que cela faisait partie intégrante de ses processus habituels de modération.

L’EPR de Flamanville est monté à 100 % de sa capacité ce week-end. Les tests vont continuer, mais une lourde opération de maintenance est déjà programmée pour septembre 2026 : 350 jours d’arrêt pour notamment remplacer le couvercle de la cuve, une petite pièce de… 100 tonnes. Le réacteur a déjà vu les délais et son coût exploser dans les grandes largeurs.
Vendredi, l‘ASNR (Autorité de sûreté nucléaire et de radioprotection) donnait son accord « pour le passage du réacteur EPR de Flamanville à un niveau de puissance supérieur à 80 % de sa puissance nominale ». En clair, le réacteur peut monter jusqu’à 100 % de sa puissance maximale de fonctionnement. On est encore loin d’une mise en production pérenne.
Au début de l’année, le réacteur avait eu le droit de dépasser les 25 % de puissance. L’ASNR avait ensuite procédé à des inspections, sans mettre « en évidence d’élément susceptible de remettre en cause la possibilité de poursuivre la montée en puissance du réacteur ». Le réacteur avait pour rappel produit ses premiers électrons en décembre 2024, après avoir obtenu l’autorisation de mise en service quelques mois auparavant. Le réacteur avait alors produit 100 MW de puissance électrique, loin des plus de 1 600 MW prévus.
Dans la foulée de l’autorisation, EDF a poussé les curseurs. Dimanche 14 décembre 2025, la pleine puissance a été atteinte à 11h37 se félicite l’entreprise : « le réacteur de Flamanville 3 […] a produit 1 669 MW de puissance électrique brute ».
On parle de puissance brute, en opposition à la puissance nette qui est celle injectée dans le réseau. EDF rappelle que la puissance nucléaire d’un réacteur correspond à la quantité totale de chaleur produite dans le cœur du réacteur par la fission nucléaire ; à ne pas confondre avec la fusion, qui est en cours de développement. La « chaleur sert à produire de la vapeur qui fera tourner la turbine. Elle est exprimée en MW thermiques (MWth) ».
Quand on parle de puissance électrique brute, c’est la puissance maximale en sortie de turbine, qui « entraîne un alternateur chargé de convertir l’énergie mécanique en électricité ». Dans la pratique, un « réacteur nucléaire consomme une partie de l’électricité qu’il produit pour ses propres besoins de fonctionnement (pompes, systèmes de ventilation, circuits de sûreté…) ».
Cette montée en puissance devait avoir lieu plus tôt dans l’année, mais un problème détecté en juin a repoussé l’échéance de plusieurs mois : « l’unité de production n°3 de Flamanville a été mise à l’arrêt dans le cadre des essais de mise en service du réacteur. Suite à des analyses, le réacteur de Flamanville est maintenu à l’arrêt pour intervenir sur des soupapes de protection du circuit primaire principal ». Tout est rentré dans l’ordre fin octobre.
Attention, le réacteur est en phase de test, la production de masse de manière pérenne n’est pas encore là. Il est question de « tester les matériels à pleine puissance, réaliser des relevés et vérifier leur bon fonctionnement ». Sur les réacteurs nucléaires, le rodage est long. Au cours des prochaines semaines, « la puissance du réacteur sera amenée à varier pour poursuivre les essais à différents paliers de puissance et une intervention sera réalisée sur un poste électrique interne ».
L’EPR va aussi avoir droit à des travaux de plus grande envergure avec le remplacement du couvercle de la cuve, une pièce de 100 tonnes et 6 mètres de diamètre. Cette opération se fera lors du premier arrêt pour rechargement du réacteur, prévu pour septembre 2026. Elle doit durer la bagatelle de 350 jours, quasiment une année complète. Le démarrage ne devrait donc pas avoir lieu avant fin 2027.
En 2017, l’ASNR avait expliqué que cette « anomalie concerne le fond et le couvercle de la cuve. L’acier de ces composants n’a pas la composition chimique attendue. Au cours de leur fabrication par forgeage, l’usine Creusot Forge d’Areva NP n’a pas suffisamment éliminé une zone qui contient naturellement un excès de carbone […]. Cette zone se retrouve donc au centre des pièces finales ».
Comme nous l’avons déjà expliqué, l’Autorité considère que, sur la base de ces analyses techniques, « les caractéristiques mécaniques du fond et du couvercle de la cuve sont suffisantes au regard des sollicitations auxquelles ces pièces sont soumises, y compris en cas d’accident ». Il fallait compter environ 7 ans pour construire un nouveau couvercle, l’ASNR avait donc donné son feu vert jusqu’à fin 2024 en attendant que la pièce soit disponible. La date limite a ensuite été repoussée.
Pour la cuve, la revue technique était arrivée à la conclusion que « l’anomalie ne remet pas en cause l’aptitude au service ». Pierre-Franck Chevet, président de l’ASNR en 2017, affirmait qu’« on peut se prononcer favorablement sur l’utilisation pérenne du fond de cuve ». Si la cuve était à changer, les coûts et les délais auraient explosé… enfin davantage de ce qu’ils sont déjà.
Le réacteur a pour rappel été mis en marche après pas moins de 17 ans de travaux (12 ans de retard sur le calendrier initial) et une explosion des coûts… c’est peu de le dire. De 3 milliards d’euros, l’addition est passée à… plus de 20 milliards d’euros.
Dans un nouveau rapport publié au début de l’année, la Cour des comptes affirmait que « les calculs effectués par la Cour aboutissent à une rentabilité médiocre pour Flamanville 3, inférieure au coût moyen pondéré du capital de l’entreprise, sur la base d’un coût total de construction estimé à environ 23,7 milliards d’euros (intérêts intercalaires compris) ». En 2020 déjà, la Cour tirait à boulet rouge sur le nucléaire français.
Récemment, RTE appelait à accélérer les usages électriques (voitures, datacenters, hydrogène) afin d’assurer un meilleur équilibre entre consommation et production d’électricité. La raison, selon RTE : une consommation « atone » depuis la pandémie de Covid-19 alors que la production d’énergies renouvelables (hydraulique comprise) et nucléaire ont progressé. La mise en marche de l’EPR de Flamanville va encore augmenter la capacité de production de la France.
Les chercheurs et chercheuses qui travaillent sur des images peuvent dès à présent les inclure dans les articles en open access en se posant moins de questions.
Le ministère de la Recherche a mis en place une « licence collective étendue » qui facilite l’utilisation d’images dans les publications en accès ouvert, explique-t-il.
Cette licence est issue d’une convention passée avec les organismes de gestion collective des droits d’auteur : ADAGP (Société des auteurs dans les arts graphiques et plastiques), SAIF (Société des Auteurs des arts visuels et de l’Image Fixe), Scam (Société civile des auteurs multimédia).
« Cette mesure bénéficie particulièrement aux disciplines où l’image est un objet d’étude essentiel, comme l’Archéologie, la Géographie, l’Histoire, l’Histoire de l’Art ou encore la Sociologie. Elle s’applique également aux Sciences, Technologies et en Médecine, lorsque les images utilisées ne sont pas produites en laboratoire », explique le ministère.

Jusqu’à récemment une telle chose n’était pas possible, mais l’article 28 de la loi de programmation de la recherche de 2020 prévoit que le gouvernement puisse prendre des ordonnances pour modifier le Code de la propriété intellectuelle « aux fins de permettre l’octroi de licences collectives ayant un effet étendu ». Une ordonnance a ensuite été prise en 2021.
Les chercheurs, notamment ceux en sciences humaines et sociales qui travaillent sur des images, devaient effectuer des « démarches complexes image par image : identification des ayants droit, demandes d’autorisation, contractualisation et paiement », explique le ministère. Désormais, ils devront seulement signaler l’image utilisée à l’aide d’un formulaire.
Pour cette licence, le ministère explique assurer « un paiement forfaitaire aux ayants droit » sans donner d’information sur le montant et les diverses conditions de la convention.
 Du côté de KIOXIA, l'amélioration des technologies et la NAND BiCS8 n'en finissent plus visiblement de repousser les limites des SSD équipés de puces QLC. Nous vous avions parlé le mois dernier du petit KIOXIA EXCERIA BASIC, un SSD NVMe d'entrée de gamme comme son nom l'indique, doté donc de NAND QL...
Du côté de KIOXIA, l'amélioration des technologies et la NAND BiCS8 n'en finissent plus visiblement de repousser les limites des SSD équipés de puces QLC. Nous vous avions parlé le mois dernier du petit KIOXIA EXCERIA BASIC, un SSD NVMe d'entrée de gamme comme son nom l'indique, doté donc de NAND QL...
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.

Ce jour, nous vous proposons de découvrir un micro à brancher à votre PC si vous avez des envies de faire du streaming ou des podcasts. Au programme, le Endorfy Solum Voice S qui se veut avant tout simple et efficace. Est-ce le cas ? Réponse ici même avec son test ici même : Test Endorfy Solum Voice S ou alors en sur la source. […]
Lire la suite
Colorful a décidé de miniaturiser ses RTX 5060 Ti et 5070, le résultat est des plus convaincants ! Les cartes se nomment iGame GeForce RTX 5060 Ti Mini et iGame GeForce RTX 5070 Mini, toutefois, il existe trois modèles puisque les RTX 5060 Ti sont proposées en versions 8 e 16 Go, toutes sont overclockées, mesurent 180 x 123 x 39.8 mm et pèsent 850 grammes. Le design est très sobre, full black, avec un ventilateur en position central et une backplate. Les cartes ont besoin d'un unique connecteur 8-pin, tout en proposant des sorties vidéo DisplayPort 2.1b (x3) et HDMI 2.1b (x1). […]
Lire la suite
Eh oui, encore une bonne grosse arnaque et avec les prix actuels de la mémoire, ce genre de pratique risque malheureusement de devenir de plus en plus fréquent. Cette fois, c'est BravoNorris qui en a fait les frais après un achat sur Amazon Espagne de quatre kits ADATA XPG DDR5-6000 en 2 x 16 Go. Des kits affichés autour de 400 euros pièce actuellement. Autant dire que la note pique déjà bien assez comme ça. Suite à la commande, trois kits ont été livrés rapidement, tandis que le dernier accusait un léger retard, le colis provenant d'Irlande. Jusqu'ici, rien d'anormal. Le premier kit est monté sans souci : aucune mauvaise surprise, tout est conforme à la commande. Mais c'est à l'ouverture du second kit, pourtant dans une boîte parfaitement scellée, que les choses se gâtent. […]
Lire la suite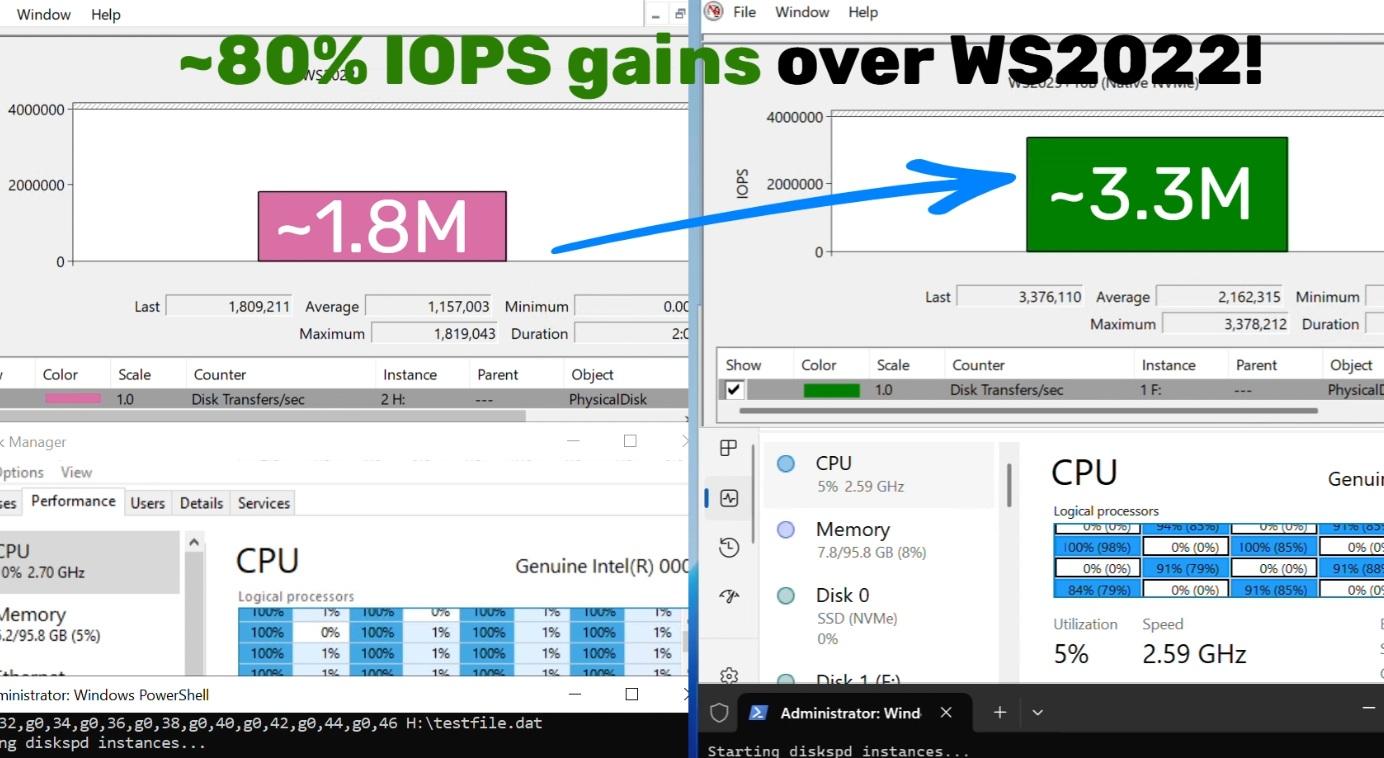 En mars et avril 2024, Microsoft faisait miroiter d’importants gains de performances pour les NVMe sous Windows Server 2025, par rapport à Windows Server 2022, grâce à une prise en charge native. Il était alors question d’une diminution de l’usage CPU, non quantifiée, assortie d’une hausse de 70 % des performances en IOPS... [Tout lire]
En mars et avril 2024, Microsoft faisait miroiter d’importants gains de performances pour les NVMe sous Windows Server 2025, par rapport à Windows Server 2022, grâce à une prise en charge native. Il était alors question d’une diminution de l’usage CPU, non quantifiée, assortie d’une hausse de 70 % des performances en IOPS... [Tout lire] 
Les jouets intégrant de l’IA générative arrivent sous les sapins. Une association américaine a testé plusieurs modèles, disponibles aux USA et en Europe. Certains robots peuvent donner des informations risquées et d’autres peuvent parler de sexe comme on ne le ferait pas à un enfant. Leur parole peut aussi pousser à une relation trop addictive et toxique au jouet.
En ces temps de fêtes et de cadeaux qui vont arriver aux pieds des sapins, la peluche qui « répond aux questions encyclopédiques » des enfants, leur « pose des questions sur des sujets scolaires », les « réconforte » et leur tient « simplement compagnie », peut être attrayante. On peut en trouver à foison sur le marché du jouet.
Mattel a annoncé en juin dernier un partenariat avec OpenAI pour de l’IA dans les jouets pour enfants. La MIT Technology Review affirmait que la marque de jouets prévoyait « d’intégrer l’IA conversationnelle à des marques telles que Barbie et Hot Wheels ». « Les premiers produits devraient être annoncés dans le courant de l’année », ajoutait le média. Rappelons que Mattel est aussi derrière la marque de jouets Fisher-Price depuis 1993.
Nous n’avons pas trouvé d’annonce dans ce sens, même si une « piste de course intelligent AI » est listée sur Amazon, mais « actuellement indisponible » :

Mais ça n’empêche pas d’autres fabricants d’incorporer de l’IA générative dans leurs jouets au risque de quelques surprises. L’association de protection des consommateurs étatsunienne PIRG vient de publier un rapport [PDF] après avoir acheté et testé plusieurs jouets, dont certains sont aussi disponibles à la livraison en France.
Dans ce document, les chercheurs de l’association rappellent que « les jouets intelligents conversationnels ne sont pas une nouveauté » et donnent l’exemple d’une Barbie lancée en 2015 par Mattel.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.