Spotify Disables Accounts After Open-Source Group Scrapes 86 Million Songs From Platform
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.

Il est 18 heures, le 24 décembre, mais vous vous rappelez qu’il manque un cadeau dans l’équation. Pas de panique, on vous a fait une sélection de vrais cadeaux qui peuvent être posés sous le sapin ce soir, à la dernière minute.

OpenAI a dévoilé son récapitulatif annuel consacré à ChatGPT. Pour l’instant réservé aux pays anglophones, ce bilan n’est pas encore officiellement accessible en France : il faut donc passer par un VPN pour en profiter. Voici comment y accéder.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.

Apple et OpenAI pourraient bientôt annoncer l'intégration d'Apple Music à ChatGPT. Le deal semble avoir été officialisé accidentellement par un responsable d'OpenAI.
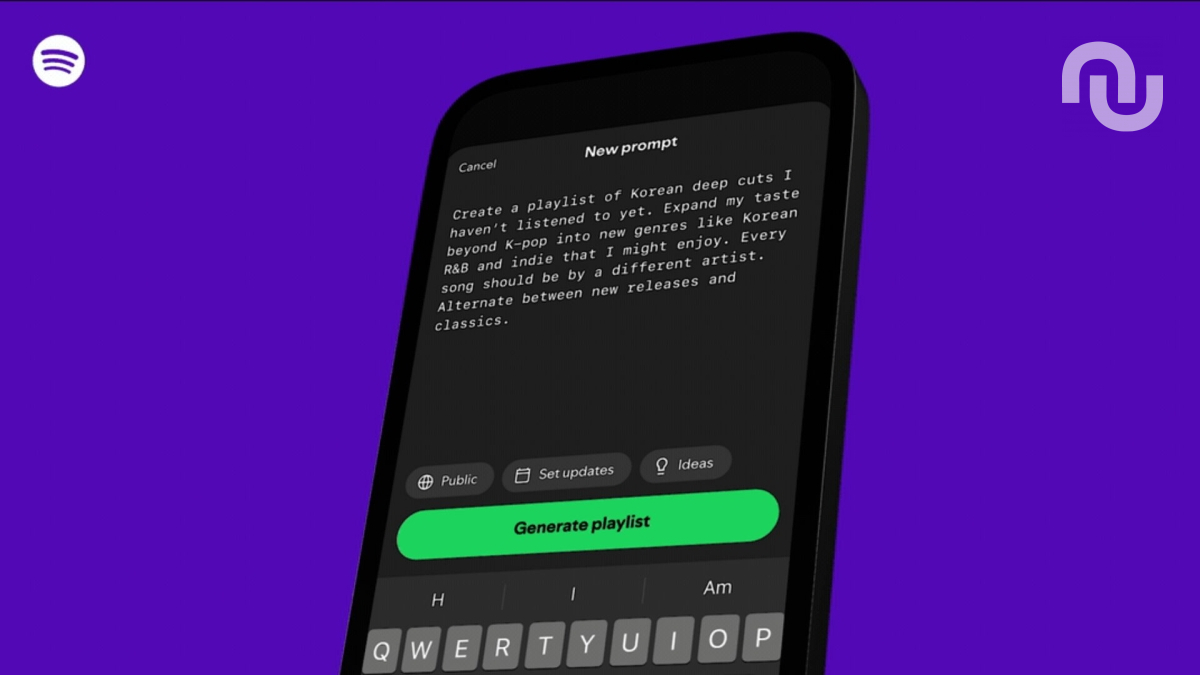
La plateforme de streaming musical Spotify a annoncé le 10 décembre 2025 une nouvelle fonctionnalité baptisée « Prompted Playlist ». Le concept : vous pourrez précisément décrire le type de playlist que vous souhaitez via un prompt, et l'IA se chargera du reste.

La célèbre rétrospective de Spotify est disponible dans l'application. Il y a deux nouveautés cette année : l'ajout des livres audio et un jeu interactif, Wrapped Party, pour comparer ses résultats avec huit amis dans une sorte de jeu interactif.

Au lendemain de la sortie du My Deezer Year et à quelques heures du Spotify Wrapped, Apple Music dégaine sa rétrospective Replay 2025. Grosse nouveauté cette année : l'intégration native complète dans l'application grâce à iOS 26, qui enterre enfin l'interface web.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.

Tous les ans, Spotify propose une rétrospective de son année dans son application. Le géant du streaming musical ne devrait plus tarder à dévoiler la version 2025 du Wrapped, qu'il commence déjà à promouvoir.