Is America's Defense Department 'Rushing to Expand' Its Space War Capabilities?
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
 Vous avez envie de profiter de la 4K (3860 x 2160 pixels) pour un usage plutôt orienté bureautique (ou jeux de stratégie pourquoi pas) et pour un tarif tout doux ? C'est possible avec le Samsung U28R550UQP qu'il est possible d'obtenir aujourd'hui pour seulement 184,99 € et avec la possibilité de se...
Vous avez envie de profiter de la 4K (3860 x 2160 pixels) pour un usage plutôt orienté bureautique (ou jeux de stratégie pourquoi pas) et pour un tarif tout doux ? C'est possible avec le Samsung U28R550UQP qu'il est possible d'obtenir aujourd'hui pour seulement 184,99 € et avec la possibilité de se...
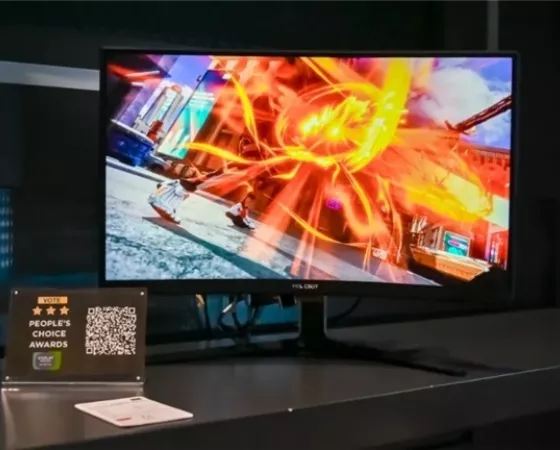 Lors de la Display Week 2024 qui vient d'avoir lieu du 14 au 16 mai 2024 à San José en Californie, TCL CSOT a présenté un écran muni d'une dalle qui a de quoi faire rêver même si la plupart d'entre nous aurions du mal à y trouver un réel intérêt. Il s'agit en effet d'une dalle affichant une définiti...
Lors de la Display Week 2024 qui vient d'avoir lieu du 14 au 16 mai 2024 à San José en Californie, TCL CSOT a présenté un écran muni d'une dalle qui a de quoi faire rêver même si la plupart d'entre nous aurions du mal à y trouver un réel intérêt. Il s'agit en effet d'une dalle affichant une définiti...
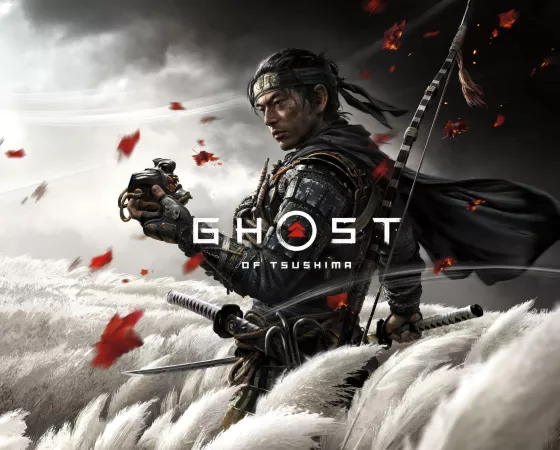 D'habitude, il faut des mods non officiels pour qu'une telle chose soit possible mais Ghost of Tsushima inaugure une tendance que l'on espère voir se généraliser à l'avenir, permettant de combiner un upscaling et un frame generation de solutions techniques différentes. Le frame generation de NVIDIA,...
D'habitude, il faut des mods non officiels pour qu'une telle chose soit possible mais Ghost of Tsushima inaugure une tendance que l'on espère voir se généraliser à l'avenir, permettant de combiner un upscaling et un frame generation de solutions techniques différentes. Le frame generation de NVIDIA,...
 L'Epic Games Store fête le lancement de ses "Méga soldes" en offrant un jeu qui mérite le coup d'œil pour les amateurs de RPG qui ne s'y seraient pas encore essayés : Dragon Age: Inquisition GOTY Edition. En bonne édition "Game Of The Year" qui se respecte, vous aurez droit à de nombreux contenus ad...
L'Epic Games Store fête le lancement de ses "Méga soldes" en offrant un jeu qui mérite le coup d'œil pour les amateurs de RPG qui ne s'y seraient pas encore essayés : Dragon Age: Inquisition GOTY Edition. En bonne édition "Game Of The Year" qui se respecte, vous aurez droit à de nombreux contenus ad...
 Jolie offre chez Cybertek si l'un d'entre vous avait dans l'idée d'acquérir une NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4070 SUPER. Grâce à un code réduction de 52 €, la ASUS GeForce RTX 4070 SUPER DUAL EVO passe de 649,99 € à 597,99 € ce qui est déjà en soi très intéressant puisque c'est tout simplement le plus bas pri...
Jolie offre chez Cybertek si l'un d'entre vous avait dans l'idée d'acquérir une NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4070 SUPER. Grâce à un code réduction de 52 €, la ASUS GeForce RTX 4070 SUPER DUAL EVO passe de 649,99 € à 597,99 € ce qui est déjà en soi très intéressant puisque c'est tout simplement le plus bas pri...
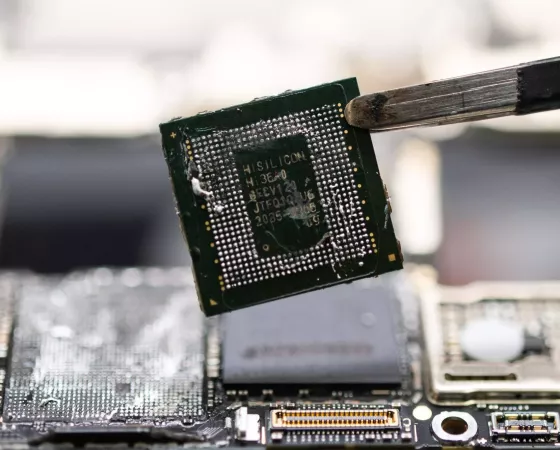 Avec sa gravure en 7 nm, le fondeur chinois SMIC a déjoué de nombreux pronostics qui voyaient la chose impossible ou en tout cas au minimum non viable. Ainsi, les fonderies de la société ont notamment sortis en 7 nm les SoC HiSilicon Kirin 9000S en 2023 puis Kirin 9010 en 2024, qui équipent des smar...
Avec sa gravure en 7 nm, le fondeur chinois SMIC a déjoué de nombreux pronostics qui voyaient la chose impossible ou en tout cas au minimum non viable. Ainsi, les fonderies de la société ont notamment sortis en 7 nm les SoC HiSilicon Kirin 9000S en 2023 puis Kirin 9010 en 2024, qui équipent des smar...
 Au Computex 2023, MediaTek et NVIDIA annonçaient leur collaboration pour mettre au point des puces dédiées au voitures, NVIDIA se chargeant d'apporter aux SoC développés conjointement son savoir-faire en matière de calculs liés à l'intelligence artificielle. Selon le média taïwanais United Daily New...
Au Computex 2023, MediaTek et NVIDIA annonçaient leur collaboration pour mettre au point des puces dédiées au voitures, NVIDIA se chargeant d'apporter aux SoC développés conjointement son savoir-faire en matière de calculs liés à l'intelligence artificielle. Selon le média taïwanais United Daily New...
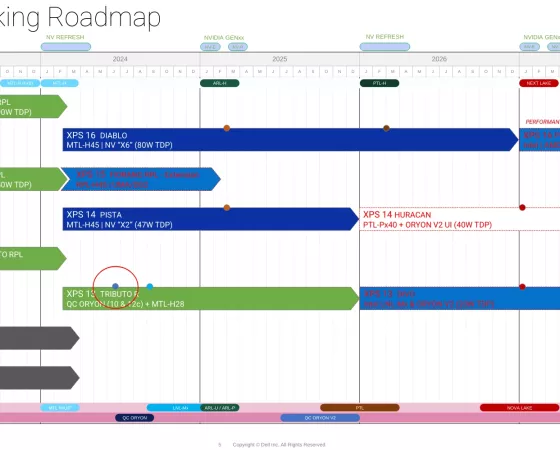 Commençons de suite à rendre à César ce qui lui appartient : la découverte du document confidentiel dont nous allons parler aujourd'hui, nous la devons à nos confrères de VideoCardz, qui sont parvenus à mettre la main sur un fichier PDF diffusé sur la plateforme Scribd depuis le mois de février pour...
Commençons de suite à rendre à César ce qui lui appartient : la découverte du document confidentiel dont nous allons parler aujourd'hui, nous la devons à nos confrères de VideoCardz, qui sont parvenus à mettre la main sur un fichier PDF diffusé sur la plateforme Scribd depuis le mois de février pour...
 Du côté d'AMD et NVIDIA, les cordons de la bourse se sont resserrés puisque nous n'avons toujours pas vu le moindre bundle offrant un jeu pour l'achat d'une carte graphique Radeon ou GeForce en 2024. C'est donc avec un certain plaisir que l'on apprend que ASUS tente de remédier un peu à cela en offr...
Du côté d'AMD et NVIDIA, les cordons de la bourse se sont resserrés puisque nous n'avons toujours pas vu le moindre bundle offrant un jeu pour l'achat d'une carte graphique Radeon ou GeForce en 2024. C'est donc avec un certain plaisir que l'on apprend que ASUS tente de remédier un peu à cela en offr...
 Voici un Bon plan très sympathique si vous cherchez actuellement un casque gaming. La boutique en ligne HyperX casse quelques prix et permet de cumuler en plus un code réduction, de quoi obtenir des tarifs vraiment exceptionnels sur trois références HyperX Cloud dont la réputation n'est plus à faire...
Voici un Bon plan très sympathique si vous cherchez actuellement un casque gaming. La boutique en ligne HyperX casse quelques prix et permet de cumuler en plus un code réduction, de quoi obtenir des tarifs vraiment exceptionnels sur trois références HyperX Cloud dont la réputation n'est plus à faire...
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.